| Smoking |
| Some people commit suicide by drowning, others by consuming poison, and still others by smoking. The only difference being that smoking not only affects the smokers but also people in the surrounding area and environment. |
Tobacco smoking related diseases constitute a major health problem all over the world.Most of the disorders linked with tobacco smoking result in various health related problems.Tobacco smoke contains more than 4000 compounds some of which are active antigenic, cytotoxic, mutagenic and carcinogenic. linked with tobacco smoking result in various health related problems.Tobacco smoke contains more than 4000 compounds some of which are active antigenic, cytotoxic, mutagenic and carcinogenic. |
| A habitual smokers’ life is shortened by about 11 minutes per cigarette smoked. The average loss of life of a smoker who smokes 16 cigarettes per day is about Six and a half year. A pack a day cigarette smoker puffs more than 70,000 times a year and thus exposes the membranes of the mouth, nose, pharynx, wind pipes and pulmonary tree repetitively to tobacco smoke. |
The three constituents of tobacco smoke that are thought to pose the greatest risk to health are:
- Nicotine
- Carbon monoxide
- Tar
NICOTINE
Nicotine, a highly toxic substance is readily absorbed from the oral, nasal and respiratory mucosa to reach the brain tissue within 7 seconds of inhalation. A smoker who smokes 20 cigarettes a day inhales 100mg of nicotine a week which in a single dose will kill him as rapidly as a bullet.
The fatal dose of nicotine is 60mg. It is a neuroendocrine stimulant and causes addiction.
CARBON MONOXIDE
A toxic gas that interferes with oxygen transport, carbon monoxide binds with haemoglobin and forms carboxy haemoglobin (C0Hb). Chronic elevated COHB leads to the occurrence of arteriosclerotic disease, coronary insufficiency, polycythaemia and impairment of skill and co-ordination. In smoking mothers it is associated with still birth, spontaneous abortions and low birth weight baby.
TAR
Tar is the aggregate of particulate matter in tobacco smoke after subtracting nicotine and moisture. It is known to cause cancer. The other major identified carcinogens in tobacco smoke are polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons, aromatic amines, nitrosamines and catechol. It also contains many potent pulmonary irritants and ciliotoxins. |
ADVERSE EFFECTS:Chronic tobacco smoking adversely affects all systems of the body.Heart: Smoking is one of t the three main independent risk factors for coronary heart disease along with hypertension and hypere-cholesterolaemia. Cardiac death rates are 60-70% greater in male smokers than in nonsmokers.Lungs: Chronic smokers show abnormalities of pulmonary function tests. Smoking causes chronic bronchitis and emphysema. It has been associated with an increased incidence of respiratory infections and death from influenza and pneumonia.Cancer: Smoking is the single most important cause of cancer.
- The risk of lung cancer is 10 times more in men who smoke one pack a day
- and 25 times more in those who smoke two packs a day as compared to nonsmokers.
- It also contributes to the development of oral, laryngeal, esophageal, gastric, pancreatic, kidney and bladder cancers.
Ulcers: There is increased incidence of gastric and duodenal ulcers and chronic mouth ulcers in people who smoke.
Stroke: It is a risk factor for development of strokes.
Plasma fats: Tobacco smoking increases the serum concentration of glucose, cortisol, free fatty acids and decreases the ratio of protective high density lipoprotein, to low density lipoprotein which is harmful.
Pregnancy: Smoking in women is associated with delayed conception and increased incidence of ectopic pregnancy. Complications of pregnancy such as Abruptio placentae, IUGR and preterm labour also increase with smoking. It significantly decreases breast milk volume and infant growth rate.
Various forms of smoking are practiced in different parts of India. Among the smoking habits, bidi takes the leading position followed by cigarette, hookah and cigar. Due to the cruder form of tobacco in bidi it has a higher concentration of tar and nicotine and thus is more carcinogenic than cigarette. |
| Nicotine being addictive, chronic smokers need adequate treatment to quit smoking. Addiction to tobacco is basically addiction to Nicotine. Smokers try to maintain thier blood nicotine levels.Of course, apart from treatment, a great amount of will power and self confidence are also needed.A diet rich in vitamin E foods such as nuts and whole grains can lower the risk of lung cancer among smokers by about 20%. |
|
 their teeth than people who do not chew.The risk of other cancers, heart disease, and ulcerative colitis is 50-70% higher among chewers.Nicotine addiction and dependence is also very real with chewing tobacco. Nicotine addiction leads to increased heart rate and blood pressure. Nicotine constricts the blood vessels and limits oxygen supply throughout the body.Chewing tobacco leaves irritating juices in contact with gums, cheeks and lips for prolonged periods of time. This can lead to a condition called leukoplakia which appears as a smooth, white patch or as leathery-looking wrinkled skin.Oral leukoplakic lesions have been seen upon continued use of tobacco use, which undergo transformation to a dysplastic state. The dysplastic lesions can further develop into carcinomas.Tobacco chewing leads to:
their teeth than people who do not chew.The risk of other cancers, heart disease, and ulcerative colitis is 50-70% higher among chewers.Nicotine addiction and dependence is also very real with chewing tobacco. Nicotine addiction leads to increased heart rate and blood pressure. Nicotine constricts the blood vessels and limits oxygen supply throughout the body.Chewing tobacco leaves irritating juices in contact with gums, cheeks and lips for prolonged periods of time. This can lead to a condition called leukoplakia which appears as a smooth, white patch or as leathery-looking wrinkled skin.Oral leukoplakic lesions have been seen upon continued use of tobacco use, which undergo transformation to a dysplastic state. The dysplastic lesions can further develop into carcinomas.Tobacco chewing leads to:



 hydrocarbons, and radiation-emitting polonium.
hydrocarbons, and radiation-emitting polonium.
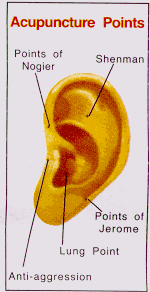 energy. The Chinese believe that Qi flows in the body through certain channels or ‘meridians’. Impaired flow leads to disease. ‘Acupoints’ are specific areas on the surface of the body which when stimulated modulate flow of Qi and influence the function of internal organs. Stimulation is achieved by puncturing the ‘acupoint’ with a needle or pressing it with the fingertip (acupressure). Doctors use special ‘maps’ that indicate the location of acupoints all over the body that can be stimulated to treat various conditions.
energy. The Chinese believe that Qi flows in the body through certain channels or ‘meridians’. Impaired flow leads to disease. ‘Acupoints’ are specific areas on the surface of the body which when stimulated modulate flow of Qi and influence the function of internal organs. Stimulation is achieved by puncturing the ‘acupoint’ with a needle or pressing it with the fingertip (acupressure). Doctors use special ‘maps’ that indicate the location of acupoints all over the body that can be stimulated to treat various conditions. linked with tobacco smoking result in various health related problems.Tobacco smoke contains more than 4000 compounds some of which are active antigenic, cytotoxic, mutagenic and carcinogenic.
linked with tobacco smoking result in various health related problems.Tobacco smoke contains more than 4000 compounds some of which are active antigenic, cytotoxic, mutagenic and carcinogenic.