| Intrauterine Contraceptive Device | |
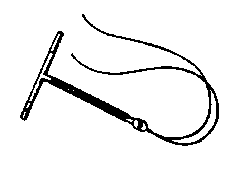
| An intrauterine device (IUD) is a small T-shaped plastic device that is placed inside the uterus to prevent pregnancy. It is a reversible type of contraception. The women having IUD in place is protected till she decides to get the device removed. The device can be kept in the uterus for 10 yrs. It can be removed early if and when the woman wants to have a pregnancy. | |
| The IUD has a plastic string is attached to its long arm end to ensure correct placement and for removal. IUDs are an easily reversible form of birth control, and they can be easily removed. However, an IUD should only be removed by a medical professional. | |
 |
 |
| IUDs are the most inexpensive long-term birth control method available.Two types of IUDs are available: copper and hormonal. The most recently introduced hormonal IUD is the levonorgestrel intrauterine system. An IUD can be placed during an outpatient visit. It can be inserted at any phase of the menstrual cycle, but the best time is right after the menstrual period because this is when the cervix is softest and when women are least likely to be pregnant.To place the IUD, a speculum is used to hold the vagina open. An instrument is used to steady the cervix and uterus, and a tube is used to place the IUD. The arms of the T shape bend back in the tube and then open once the IUD is in the uterus. Once the IUD is in place, the instruments are withdrawn. The string hangs about an inch out of the cervix but does not hang out of the vagina.
Women should never try to remove an IUD themselves. A clinician can usually remove an IUD very simply by carefully pulling the string ends at a certain angle. This causes the IUD arms to fold up and the IUD to slide out through the cervix. |
|
| The arms of this IUD contain some copper, which is slowly released into the uterus. The copper prevents sperm from making their way through the uterus into the tubes and prevents fertilization. If fertilization does occur, the copper prevents the fertilized egg from implanting on the wall of the uterus.Hormonal IUDs that contain progesterone must be replaced every 5 years. They can be removed at any time if a woman decides she wishes to become pregnant or if she does not want to use it anymore. Hormones are in the arms of the IUD and are released slowly into the uterus. The hormone used is mostly levonorgestrel, which is similar to progesterone. It causes cervical mucus to thicken to prevent sperm from entering the cervix and reaching the egg. | |
| Contraception | |
Intrauterine Contraceptive Device
Reply

 Emergency contraceptive pills are sometimes called the morning-after pill. This pill has to be taken within 72 hrs of unprotected sex. These pills contain high doses of the same hormones that are in birth control pills.It is mostly a single doses product. But some brands have to be taken as 2 doses, 12 hrs apart. One must follow the advice available with the pill.
Emergency contraceptive pills are sometimes called the morning-after pill. This pill has to be taken within 72 hrs of unprotected sex. These pills contain high doses of the same hormones that are in birth control pills.It is mostly a single doses product. But some brands have to be taken as 2 doses, 12 hrs apart. One must follow the advice available with the pill.
 introducedinto vagina, it kills and immobilizes the sperms. Example of spermicide is Delfen Cream. It is a white cream with 5% nonoxynol 9 as spermicide. A plastic applicator with piston is used which is screwed to the mouth of the cream tube. The cream tube is pressed to fill up to the mark of 2.5 ml. The women lies on her back with knees pulled up, separates her labia minora by left thumb and index finger and pushes the cream filled applicator inside vagina as high up as possible. The cream is delivered by pressing on the piston. The cream is introduced 3 minutes before coitus.
introducedinto vagina, it kills and immobilizes the sperms. Example of spermicide is Delfen Cream. It is a white cream with 5% nonoxynol 9 as spermicide. A plastic applicator with piston is used which is screwed to the mouth of the cream tube. The cream tube is pressed to fill up to the mark of 2.5 ml. The women lies on her back with knees pulled up, separates her labia minora by left thumb and index finger and pushes the cream filled applicator inside vagina as high up as possible. The cream is delivered by pressing on the piston. The cream is introduced 3 minutes before coitus.